The theory of Darwinian evolution includes self-replication, mutation, and the interaction of living organisms with the external environment. Recently, quantum machines have started to mimic these actions by following certain patterns of biology.
The aim of such models is to reproduce the characteristic processes of evolution, adjusted to the world of quantum algorithms and quantum computing.
Can There Be Life Inside A Computer?
The concept of the current innovation is based on the relationship between the randomness we see in our everyday lives and the probabilistic representation of the information inside the quantum world, at a micro and macro level. There is a relationship between quantum mechanics and the encoding behavior of life, such as natural selection, learning, memory, and intelligence.
Therefore, scientists have started to design quantum information protocols, the potential of which are analogous to these characteristics. This has further led to the development of the concept of quantum biomimetics.
This research uses the IBM QX4 quantum computer to code units of quantum life created by two qubits. The first qubit represents the genotype, the genetic code passed between generations. The second qubit represents the phenotype or the outward manifestation of the "body," as a result of the organism’s environment. Just as any living being, these units were programmed to mimic encoded behaviors like reproduction, mutation, evolution, and death.
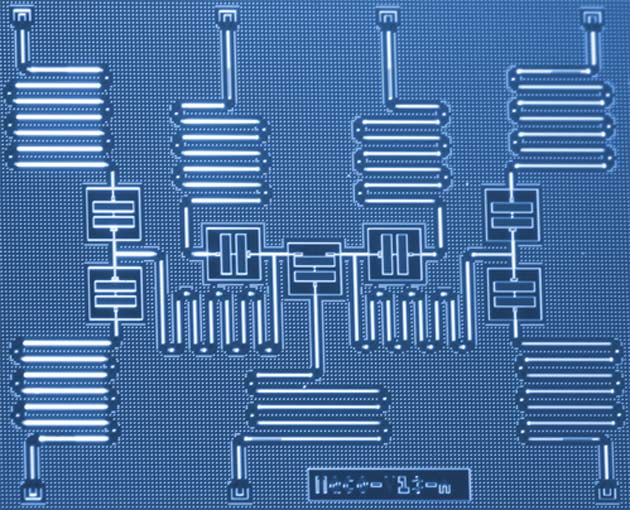
Two such qubits of the IBM QX4 quantum computer were used to code units of quantum life. (Source: IBM)
Explanation for the Origin of Life & Evolution
In the study, every representation of evolution was based on quantum behavior such as the use of the characteristic quantum mechanics phenomena (e.g., entanglement). Behavior from a living organism was embedded into the structure of quantum algorithms. For example, for the mutation process, the algorithm was based on the rotation of the quantum state.
The components (i.e., the life) of this development have a finite lifetime.
However, the system is autonomous so it can learn from the mechanism that is designed. With respect to natural selection, Unai Alvarez-Rodriguez, a researcher at the Quantum Technologies for Information Science (QUTIS) and an expert in quantum information technologies, said, "More than anything we have come up with a quantum mechanism on which self-replicating systems could be based and which could be used to automate processes on a quantum scale. And finally, as regards learning, we have come up with a way of teaching a machine a function without having to insert the result beforehand. This is something that is going to be very useful in the years to come, and we will get to see it."
The IBM supercomputer used in this research only partly counted as a full quantum computer, which is currently beyond our technological reach. Although, these machines are getting more powerful with the passage of time.
But whether or not the origin of life was genuinely quantum mechanical remains an open question.
The basis of this innovation is that microscopic quantum systems can encode biological behaviors related to living systems and natural selection.
IBM, Google, and others are working on systems that could exhibit quantum supremacy, and they are planning to have these models available to cloud users within a few years.
“We only have to look at ourselves to see how intelligent life might develop into something we wouldn't want to meet.” - Stephen Hawking
Top Image: Researchers, have, for the first time ever, created artificial life inside a computer. (Source: Vladimir_Timofeev/iStock/ScienceAlert)
References
- Scientists Just Created Quantum Artificial Life For The First Time Ever, 2018, ScienceAlert, https://www.sciencealert.com/scientists-simulate-artificial-life-in-quantum-algorithm-for-first-time
- Unai Alvarez-Rodriguez et al. (2016), Artificial Life in Quantum Technologies, Scientific Reports
- University of the Basque Country, 2017, Artificial Intelligence in Quantum Systems, too, Phys.org, https://phys.org/news/2017-02-artificial-intelligence-quantum.html
- Scientists Just Took a Big Step Towards Creating Artificial Life, 2017, ScienceAlert, https://www.sciencealert.com/yeast-genome-synthesis-brings-scientists-another-step-closer-to-creating-artificial-life
- Scientists Create Quantum Life on Five-Qubit IBM Computer, 2018, Top 500: The List, https://www.top500.org/news/scientists-create-quantum-life-on-five-qubit-ibm-computer/






No comment