Matter & Energy
A New Brain Implant Can Translate Thoughts Into Speech
A new study demonstrates that electrical activity in the brain can be decoded and used to synthesize speech. This research may, one day, give a voice to the people who have lost speech by way of neurological disorders.
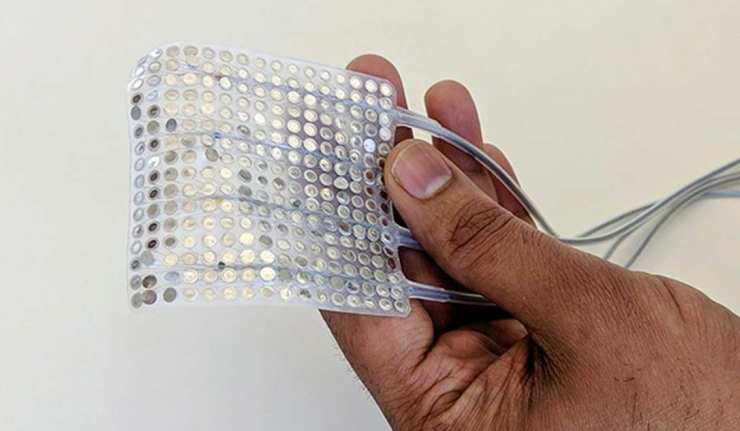
Graphene Makes It To The MWC: ICFO Shows Off Next-Gen Wearables And Sensors
Graphene could be the material of the future. It has already demonstrated promise in a wide range of beneficial applications, from energy storage to water purification.
Perovskite, The New LED? Reports Have Come In Of The Most Effective Next-Gen Light Source Yet
LEDs may be the future of lighting. While they may be slowly losing out in terms of screen technology composition to their organic counterparts (i.e., OLEDs), they are low-energy, energy-efficient and increasingly long-lasting. Therefore, they may ultimately replace more traditional solutions such as bulbs in homes and business.
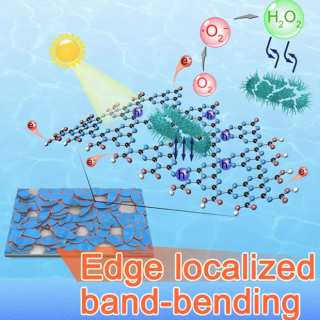
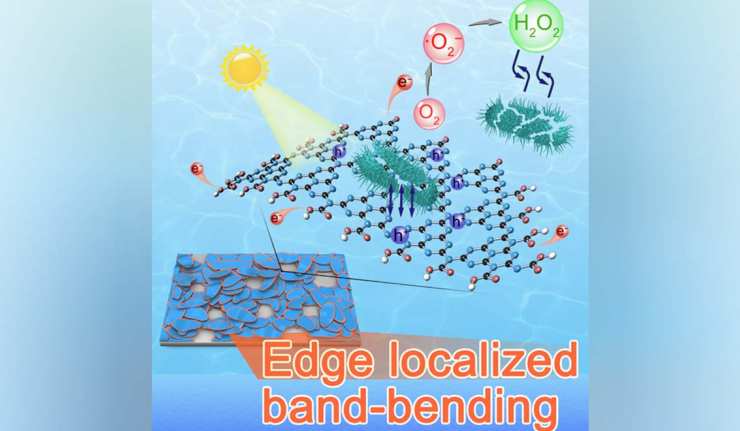
New Solar-Powered Graphite Derivative Allegedly Purifies Water in Minutes
The availability of clean drinking water may become an increasingly pressing issue. It is already a critical problem for many people right now. 29% of the world’s population lack consistent access to this supposedly simple resource in their own homes or communities.
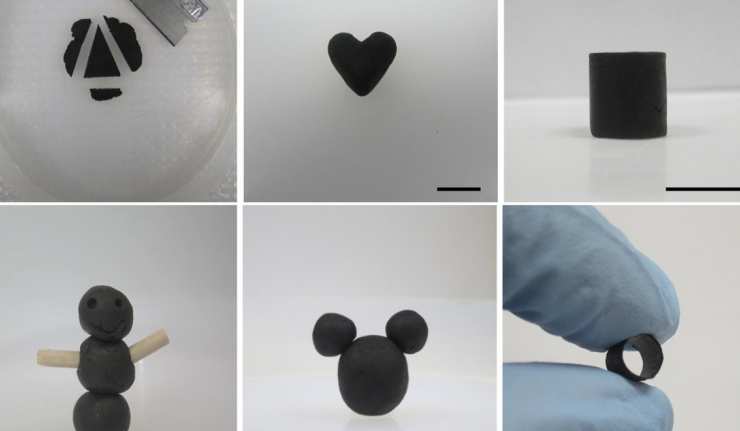
Graphene Play-Doh: New Plasticine-Like Formulation Could Significantly Boost Graphene Industry
Graphene is a nanostructure for carbon atoms that arranges them into two-dimensional sheets in a regular hexagonal pattern. Due to its molecular, electrochemical and physical properties, it could have an essential role to play in the future of technology.
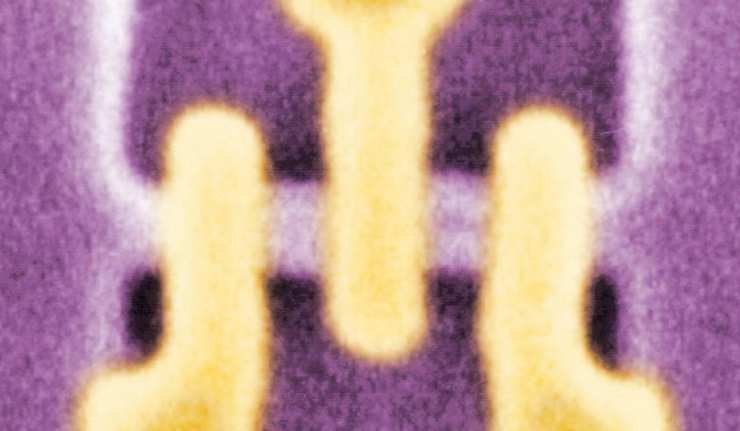
New Breakthrough May Bring Electronics Closer To The Atomic Scale
Personal electronics have become a veritable way of life for many people around the world since they are used for work, communications, scheduling, and entertainment on a regular basis.
MIT Scientists Claim First Successful Fuel-Free, Engine-Free Ion-Powered Flight
What if powered mechanical flight didn’t require all the normal trappings of aircraft? That is, a flight that does not need big heavy jet engines to get a plane off the ground, or tons of octane to power this propulsion? Well, some engineers and scientists assert that this arrangement isn’t actually necessary for the purpose of artificial flight at all.
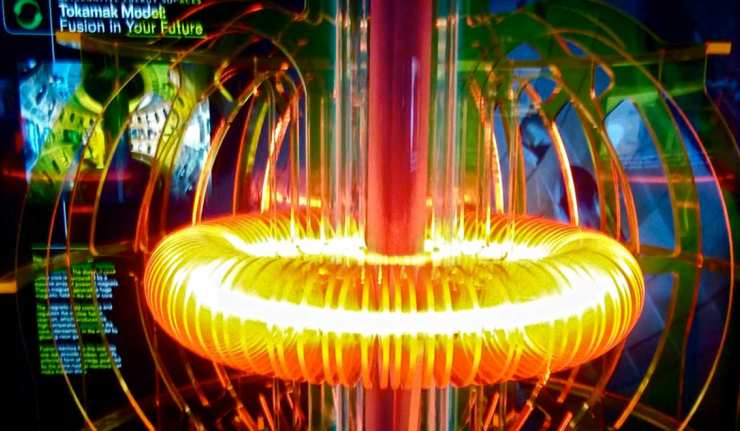
Nuclear Fusion Edges Closer: Chinese Tokamak Facility Can Heat Plasma To Hotter Than 6 Suns
Nuclear fusion could be the large-scale energy source of the future. It is a relatively clean form of power that is associated with potentially huge output and could, thus, serve more people for longer compared to traditional methods. On the other hand, this form of energy has also become linked with a reputation for various dangers in the public eye.
Could This Be The ‘MoST’ Effective Way To Bottle Sunlight? Swedish Researchers May Have Solved Our Solar Energy Problems
Electricity as a result of converting sunlight into usable energy is fairly straightforward, but, so far, mostly only in theory. This process follows a general hypothesis -- the sun provides all the energy that humanity needs, and more, in the average year. Therefore, capturing this light using equipment such as solar panels could resolve the global 'energy crisis' immediately.
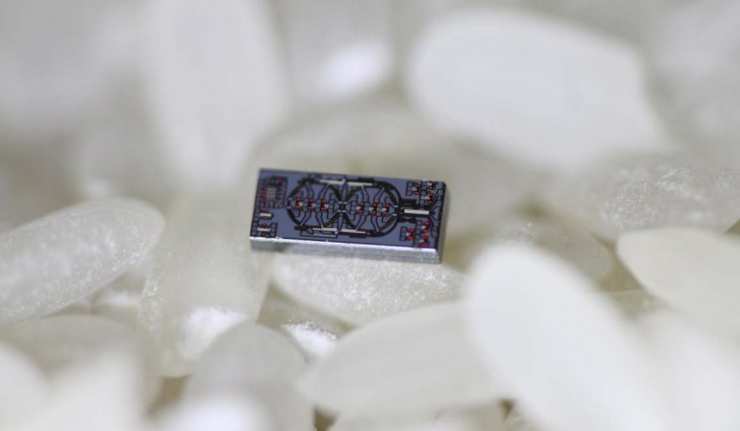
New Type of Gyroscope is Smaller Than Grain of Rice
How does your phone flip into landscape mode or come alive when you pick it up? It has a gyroscope, which is a particular type of sensor that lets electronic devices know which way is 'up!'
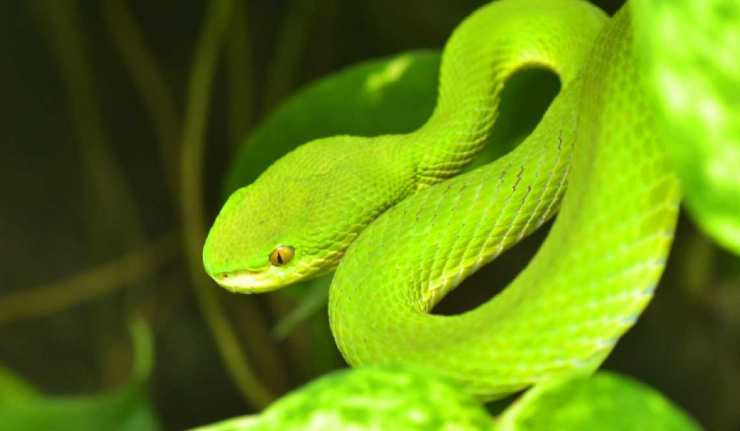
Engineered Nanoparticles Designed To Effectively Treat Snakebites
As of February 2018, the World Health Organization (WHO) has estimated that approximately 5.5 million people are bitten by snakes each year, and about 2.7 million contracts a deadly disease called snakebite envenoming. This is an issue in most tropical and subtropical regions of the world. Asia takes the top spot as far as envenoming goes, with 2 million affected annually, most of these individuals are from low- to middle-income countries where healthcare resources are limited.
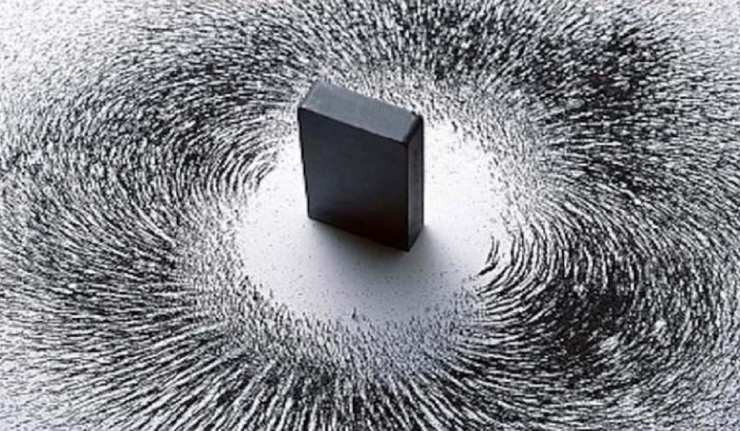
Single-Molecule Magnet Produced At Record High Temperature
Physicists have developed compounds that can ‘record’ the direction of the last magnetic field they have experienced. This property, known as magnetic hysteresis, comes into effect after the substances have been exposed to magnets for an appreciable length of time, and it persists even after the magnetic field has been withdrawn. The property of magnetic hysteresis is interesting from a basic scientific standpoint.
New Breakthrough Technique Lets Scientists See One Molecule Through The ‘Eyes’ Of Another
Molecules, or singular units of substances such as proteins or gases, react to each other through a complex, and finite, set of properties. These include the electrical attributes that may repel or draw one atom away from (or toward) another; electrical charges acting on different chemical bonds, as well as a number of other smaller forces often named after the scientists who discover them (e.g., Pauli or Stark forces). These factors determine how different molecules interact, and, ultimately, build up what we think of as the matter around us.
There Is A New World Record For Superconductivity!
Superconductors are something of a holy grail to electronic scientists and engineers. They are materials that conduct electricity in the absence of resistance. This property, while vital to certain components and techniques, is largely responsible for losses and limits to the movement of electrons on which modern automatic, computerized and mechanized devices depend. The ability to produce superconductors that could work in ambient conditions could usher a new revolution in these products, their capabilities, and power, in general.
Can Liquid Fuel Be Electric Too? New Research Suggests That Cars Can Be Powered By New Ionic Fluid
Electric cars may seem like an attractive departure from concerns about traditional fossil fuels and the environmental impact their use can impart, not to mention the costs that are involved.
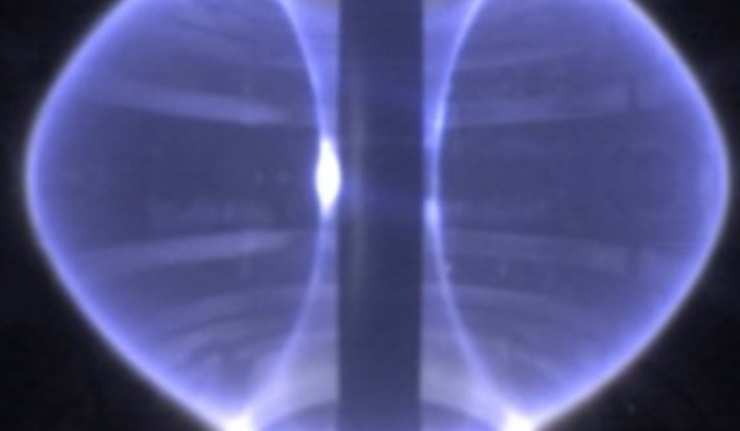
Magnetic Flux Capacity: New Research Shows How To Improve Nuclear Fusion Reactions
Nuclear fusion is a concept for power generation that has been around for some time. These days, research and development in this area are done using up-to-date reactors called tokamaks. These installations may provide the data and insights necessary to bring fusion back into the 21st century.
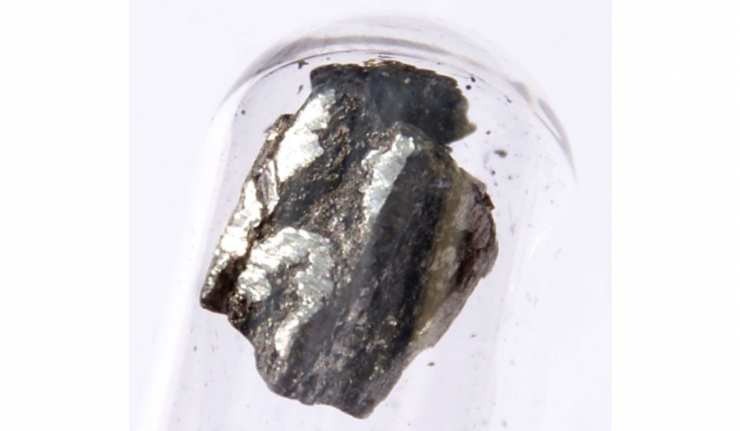
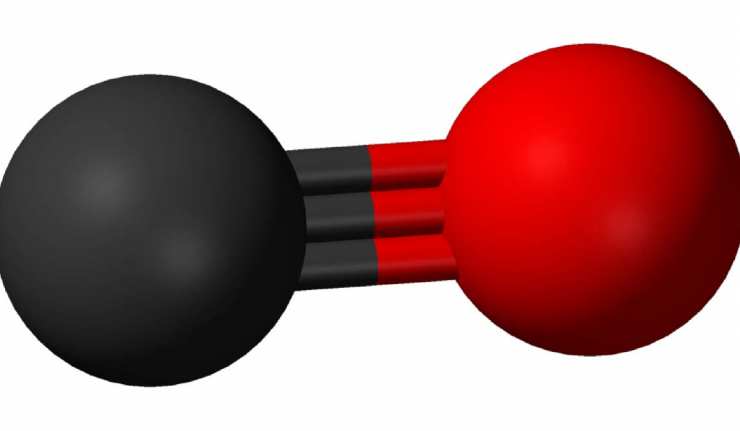
Gold-Palladium Alloys Are Better For Hydrogen Storage, And Now We Know Why
Hydrogen is a leading contender for the energy source of the future. However, the technology behind its delivery and deployment is nowhere near consumer-level yet. Hydrogen-power scientists are still working out issues to make their solutions safer and more efficient. One of the factors holding hydrogen back is the puzzling inability to get the substance to stay in the storage media intended for it.
How To Stop Ice? New Research Re-imagines Anti-Freeze In Nature
It is fortunate that scientists discovered anti-freeze proteins (AFPs). Otherwise, the way in which insects survive freezing conditions would be an impenetrable mystery to us. Insects lack things such as hair, fur or blubber, therefore, making it impossible for them to live in cold climates without AFPs. These proteins have evolved to prevent lethal ice crystals forming within insect bodies. For a long time, this phenomenon was explained using the ‘anchored clathrate’ theory of water molecule ordering.
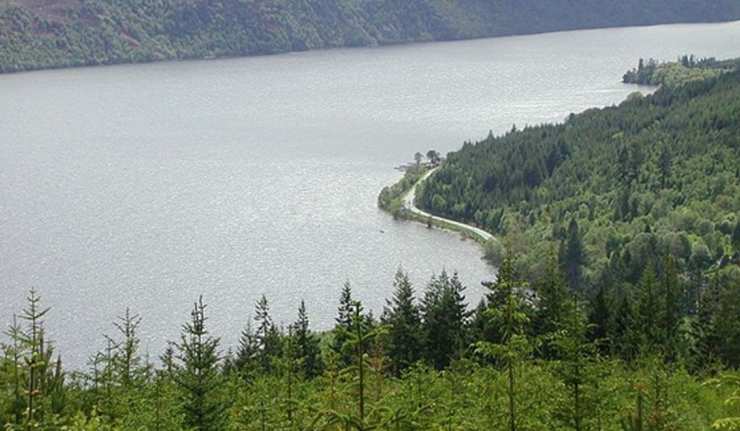
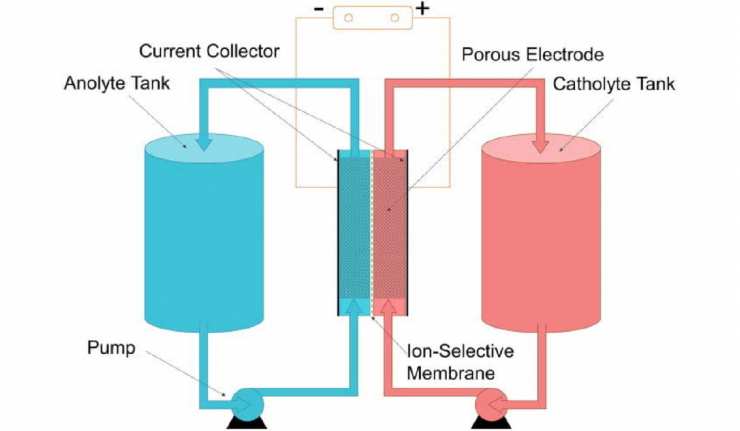
New Proposed Project Could Turn Loch Ness Into Monster Power Source
Scotland is a good example of a country that is making a commitment to a future with greener, more sustainable energy. The nation has increased its volume of off-shore wind farms by 37%, recently. However, this investment only means so much in the context of the weather. In calm weather, Scotland may need back-ups in the form of batteries in order to keep constant the current flowing through its grid.
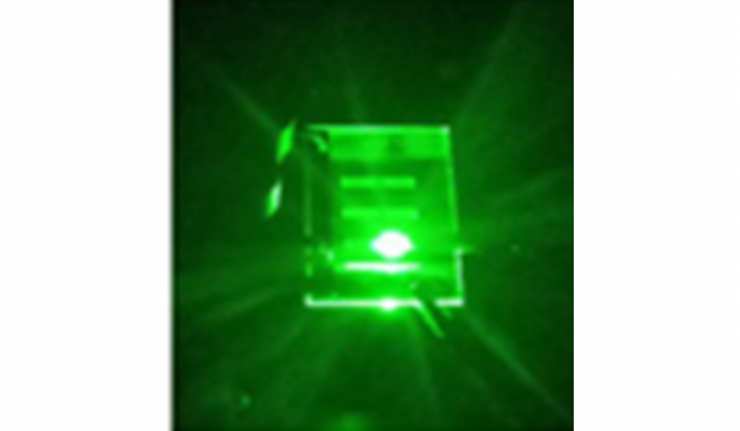
New Research Shows That Quantum Networks Are Worth (Synthetic) Diamonds
It seems that diamonds grown in a lab will have many roles to play in the electronics and engineering of the future. This could be because these precious stones contain (necessary) defects, often worked into the diamonds to order.
The defects are created when a non-carbon atom takes the place of a carbon atom in the orderly molecular lattice that normally makes a diamond. Nitrogen vacancies (NVs), for example, have drawn some attention due to their potential in diagnostics, and their ability to emit red light when green light hits them, which has potential analytical value.