Bioengineering
Chinese Scientists Make Monkeys “Smarter” in a Controversial Experiment
For the first time, Chinese scientists have used gene-editing techniques to make monkey brains more humanlike. The rhesus macaques got "smarter" as they were found to have superior memories to unaltered monkeys, according to a recently published research that has kicked off a fiery debate among ethicists about how far scientists should be able to take genetic experimentation.
New Insight Into Our Brain’s Networks And The Human Consciousness
A new study, published in Science Advances, has uncovered networks in the brain that are at work when we are conscious. Scientists have been preoccupied with understanding consciousness for centuries. Modern brain imaging techniques are starting to lift this uncertainty, and providing unprecedented insight into the human consciousness.
Biologists Find Glutamate-Based Long-Distance Signaling Is Rapid In Plants
Plant biologists have discovered that when a leaf gets eaten, it warns other leaves by using some of the same signals as animals. This new work is starting to unravel a long-standing mystery about how different parts of a plant communicate with one another. A plant injured on one leaf by a nibbling insect can alert its other leaves to begin anticipatory defense responses.
Battery Pharma: Can Genetically Modified Chickens Really Produce Viable Medicines?
Currently, the pharmaceutical industry makes billions of dollars from the compounds it produces in factories specially designed for the various chemical processes involved in doing so. These manufacturing processes are expensive, time-consuming and can be a source of pollution. However, lately, many drug types (particularly those based on or derived from natural antibodies) can be ‘grown’ in bacteria or bacteriophages engineered to express these proteins from their own DNA.
Perfect Blood Vessels Grown In Petri Dish May Help Millions Of Diabetic Patients
Diabetes is a condition associated with an acquired or inherent resistance to the effects of insulin. The resulting metabolic disruptions can have knock-on effects on various tissues types, most notably blood vessels. This gradually prevents them from ferrying oxygen and nutrients to the body, which can become particularly hard on internal organs and parts of the circulatory system that are far away from the heart.
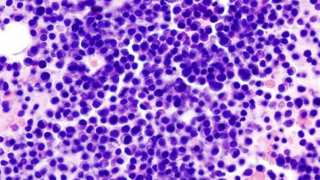
Latest Technology Can Identify Multiple Myeloma Cells Faster Than Ever
Multiple myeloma is a type of blood cancer that affects the plasma cells located in the bone marrow of the body. During an infection, when B cells or B lymphocytes mature, they become plasma cells, which, in turn, are responsible for the production of antibodies or immunoglobulins. Therefore, multiple myeloma is a condition when these plasma cells grow uncontrollably and become cancerous, also producing abnormal proteins like monoclonal immunoglobulin. Ultimately, the excessive proliferation of cells leads to organ failure and death.
CRISPR-Engineered Hybrid Rice Plants Can Now Clone Their Own Seeds
The USDA has defined food insecurity as the lack of consistent access to food to sustain a healthy living. An estimated 1 in 8 Americans, including about 12 million children, were found to be ‘food insecure,’ in 2017, according to a recent paper published by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
The ‘CRISPR Babies’ Story: A Recurring Ethical Nightmare
Not long ago, a scandal surrounding the claims made on the part of the genetic scientist, He Jiankui, made headlines. It involved public announcements of the successful editing of the genome in a pair of twin girls born as a result of in vitro fertilization (IVF). Jiankui asserted that this was indeed done at the stage at which the embryo that eventually gave rise to the babies via CRISPR-Cas9 editing.
New Study Shows Error Recognition In Humans Traced To Single Neurons
It is clear that mistakes are somehow registered and processed in the brain. This is because errors result in behavior-based reactions such as moving to correct them and slowing down slightly while working so as not to risk making them again. As the links between such observations or perceptions are made in the brain, it follows that this organ controls the recognition and responses to errors in the people who make them.
Baby Born Out of Womb Transplant from Deceased Donor, for First Time Ever
It has been estimated that infertility, or the inability of a person to conceive by natural means or stay pregnant, affects as many as 15% of couples in the US at reproductive age. Also, 1 in 500 women has uterine infertility, which could be caused by reasons such as defects at birth, injury or infection.
Mammalian Analog for Royal Jelly Protein Found, and Could Revolutionize Stem Cell Science
Royal jelly is of potential interest to researchers in the areas of regenerative medicine and science. This compound is secreted by honey bees (Apis mellifera) and functions to transform ordinary bee larvae into queen bees. This process is most likely done by certain molecules in the jelly, which is known to act in an epigenetic manner.
‘Genetically Modified Babies’ Claim May Ruin Chinese Scientist’s Career
He Jiankui, a geneticist affiliated with China’s Southern University of Science and Technology, rocked the scientific world with an outlandish claim of having edited the genes of IVF (in vitro fertilization)- generated embryos, last week. However, his story has not had the reception he may have hoped.
Bionic Yeast: Single-Cell ‘Biofactories’ Get Nanotech Enhancement To Make Them More Energetic
The use and cultivation of yeast are possibly one of the oldest forms of biotechnology known to humanity. People have been leveraging its natural properties to make products such as bread and beer for generations. In the modern era, scientists have also found that yeasts can be engineered to produce drugs, using chemicals and other industrially important molecules.
Breaking New ‘Grounds’: Technology Developed To Detect On-Field Sports Concussions
Given the consistent popularity of contact sports such as rugby or American football, concussions should be a persistent concern for its players, coaches, colleagues, and fans as well.
Origin Of Life: Simple Chemicals On Early-Earth Can Produce RNA’s Building Blocks
The origin of life on Earth is believed to be a set of paradoxes. In order for life to have gotten started, there must have been a genetic building block, such as DNA or RNA, which was capable of passing along the blueprints for making proteins, the 'workhorse' molecules of life. Recently, a team of researchers has shown for the first time that a set of simple starting materials, which were likely present on early Earth, can produce all four of RNA’s chemical building blocks.
World’s First ‘Test Tube’ Lion Cubs Born In South Africa
Artificial insemination is a well-validated technique to help individuals or couples who are having trouble conceiving on their own. However, there may now be evidence that this method could be practiced by scientists and conservationists to address the scarcity or near-extinction status in various species.
Implant Helps Paralyzed Spinal Cord Injury Patients Move Again
The National Spinal Cord Injury Association has estimated that about 450,000 people in the United States are living with spinal cord injury (SCI).
Scientists Have Measured The “Speed Of Death” For The First Time Ever
There are certain cascading waves in all multicellular organisms — trigger waves — that form an integral part of the biological process of cells. These waves are involved in the transmittance of information over long distances. For example, in the brain, trigger waves help in the movement of electrical signals along the axons and act as neuron action potentials. Similarly, the waves are also known to be involved in the cell cycle.
Spinal Neurons Grown From Stem Cells For First Time
Modern medicine has still not managed to crack the problem of spinal cord injuries that result in significant paralysis or loss of functional status. There are numerous factors that influence the inability to restore movement or autonomous bodily control to these patients. A prominent example of these is the inability to cultivate new neurons that make up and power the spinal cord. However, some researchers have claimed that they have successfully induced ‘generic’ human stem cells to differentiate into stem cells that apply more specifically to the spine.
Lab-Grown Lungs, Shown To Work As Intended, In Large Animal Model
The availability and viability of live human organs for transplantation into needy recipients is a considerable healthcare problem. Reports suggest that there are over one thousand names on the waiting list for lung transplants in the United States alone. Therefore, bioengineered organs for alternative donations may become necessary. They are also steadily becoming more feasible than ever before.