earth
The Climate Crisis: Carbon Dioxide Concentration Highest in 3 Million Years
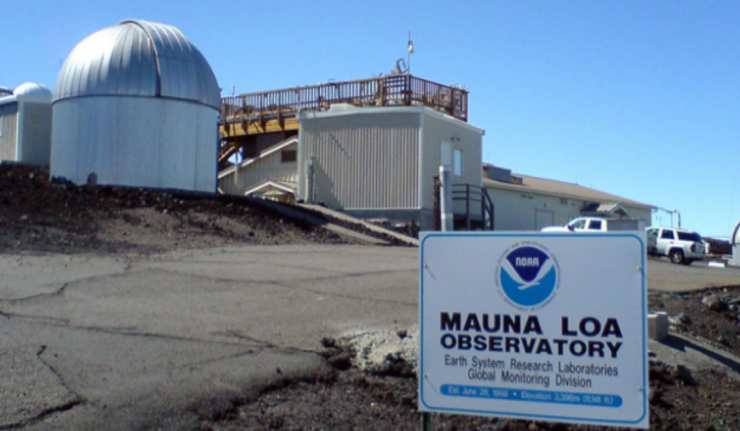
Atmospheric levels of carbon were registered at 415 ppm for the first time in three million years. This number was measured at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. The measure continues the upward trend of atmospheric carbon concentration that lies at the heart of global warming and the climate crisis.
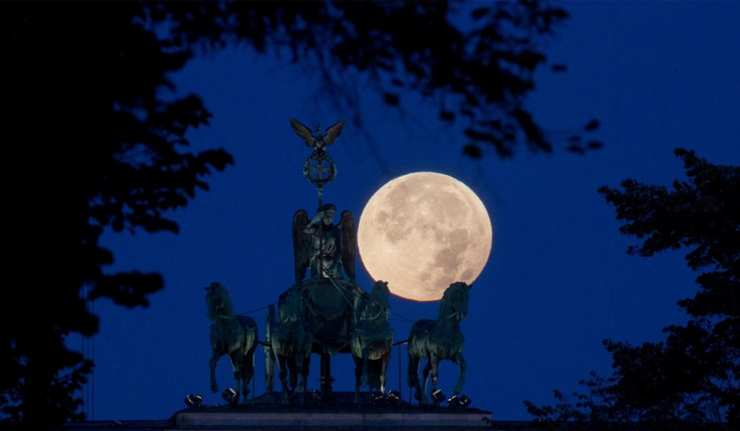
Tonight’s ‘Super Snow Moon’ Could Be A Celestial Treat
Tuesday (Feb 19, 2019) will bring with it, the “super snow moon.” This moon will be at its closest to Earth at 4:07 am EST (0907 GMT).
A 'supermoon' occurs when a full moon coincides with the moon's perigee, or the point in its elliptical orbit at which it is closest to the Earth. This makes the moon appear up to 14 percent larger and 30 percent brighter than usual. We, earthlings, see this event when the moon is full or nearly full and also at its closest point to our planet, along with its slightly elliptical orbit. This close approach is called perigee by astronomers.
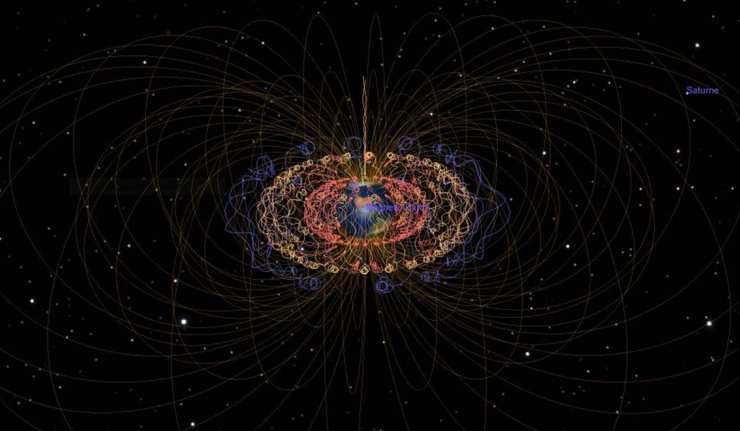
The Earth’s Magnetic ‘North’ Pole Has Officially Shifted
The geomagnetic field, simply known as the Earth’s magnetic field, is one that extends from Earth to space, and its magnitude has been estimated to be between 25 and 85 microteslas (i.e., 0.25 to 0.65 gauss). The North Pole is in the Northern Hemisphere while the South Pole lies on the opposite side in the Southern Hemisphere, and it is between these poles that a magnetic field, by electric currents, is generated.
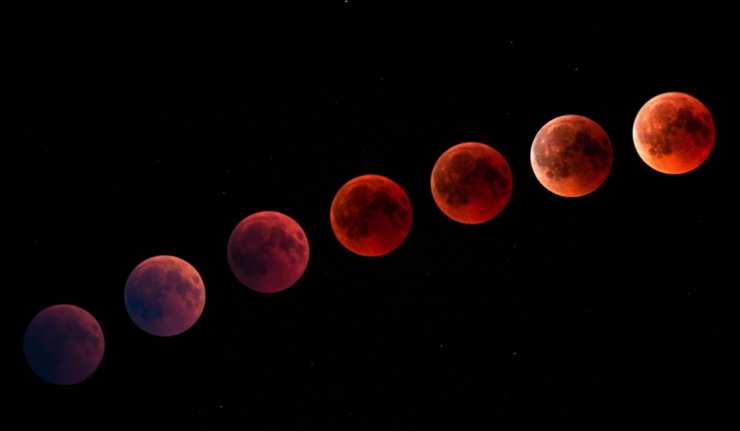
Weekend’s Super Blood ‘Wolf’ Moon Was Also Decade’s Last
Astronomers and lunar scientists had calculated that there would be a spectacular blood moon on January 18, 2019. These events are given the name because the moon turns a strong red color before falling into a complete eclipse. However, this was a more than average lunar occlusion. The satellite was also at the closest point to the Earth, as it began this eclipse, thus upgrading its status to a ‘super’ blood moon.
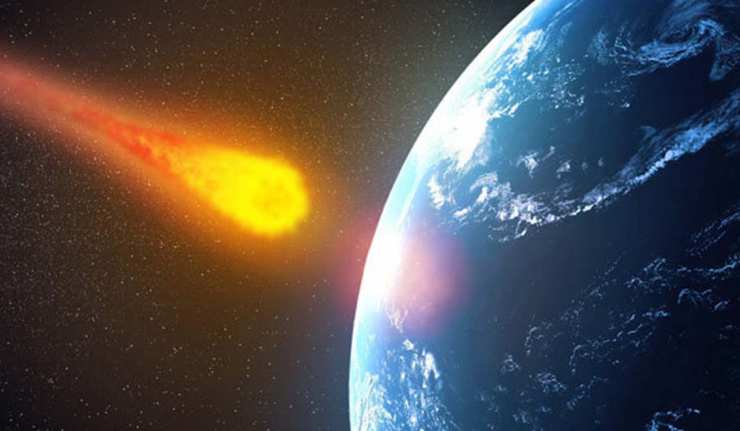
A Few Days Ago, Asteroid ‘2019 AG3’ Narrowly Missed The Earth’s Surface
Asteroid AG3 missed the Earth by more than three million miles (4.9 million km), 12.86 times the distance from Earth to the moon, which may be considered a narrow miss on the cosmic scale, especially given the speed of space rocks.
A giant asteroid dubbed Asteroid 2019 AG3, a massive space rock, flew past Earth on Monday (Jan 14, 2019), in the early hours of the morning (GMT), according to NASA.
The Milky Way May Collide With A Second Galaxy Soon
What will happen to our galaxy in the future? Astronomers actually have a relatively detailed picture of what may happen to the Milky Way, through scientific and mathematical models of this galaxy. This data indicates, for example, that our galaxy will collide with its near neighbor, the Andromeda, at some point. However, this is not thought to be likely to occur for about eight billion years, by which time humanity may or may not even exist.
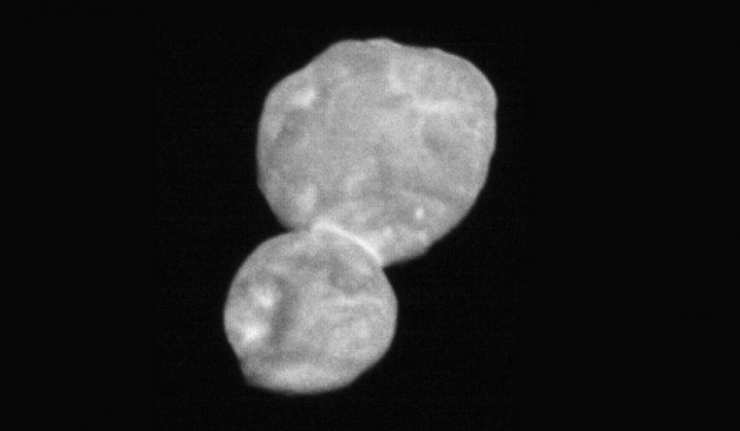
New Horizons’ Data Results in Clearer Picture of its Far-Flung Target
A few days ago, NASA presented footage of its craft, New Horizons, as it completed a fly-by of a specific object in the Kuiper Belt. This mission was a success as the vessel was able to capture images and data on its target a certain amount of accuracy.
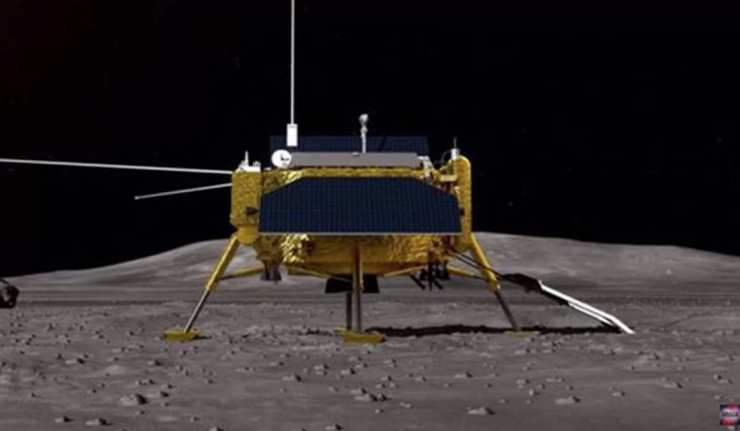
China Claims World-First Spacecraft Landfall on Far Side of the Moon
According to reports coming from the Chinese aeronautical authority, CNS, human exploration has pushed another frontier for the first time. This undiscovered country is the ‘far side’ of the moon, which is normally never seen by anyone but is thought of as containing pristine insights into life in the early days of the solar system that are not found on Earth.
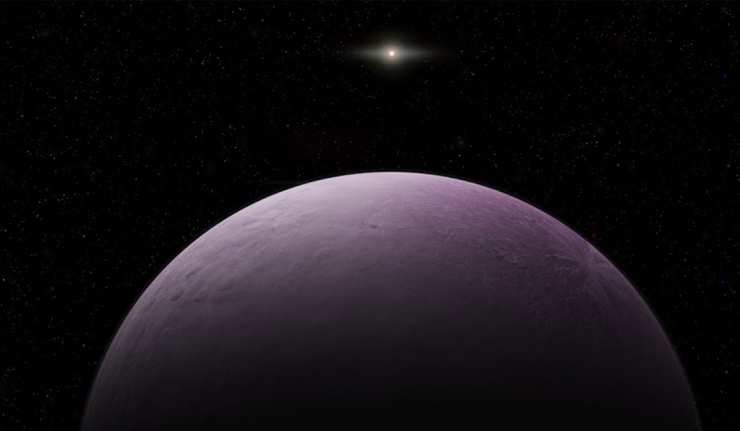
10th Planet in our Solar System? The Newly Discovered “Farout” Has A Pinkish Hue
There’s a new dwarf planet in our solar system, and it’s the most distant one scientists have ever discovered. This tiny world, formally known as 2018 VG18, but nicknamed Farout, is about 18 billion kilometers away, roughly 3.5 times the distance to Pluto from Earth. The pink cosmic body was nicknamed after its discoverer’s exclamation!
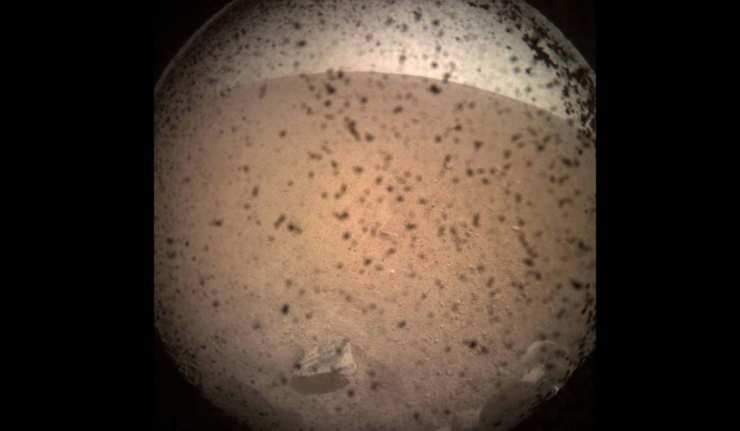
Highlight Of The Week: NASA’s InSight Makes Flawless Landing On Mars
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory’s (JPL) mission support center was a hive of activity and nerves, a few days ago, as the InSight team monitored the fate of the craft this project had revolved around for years.
Meteor Explosion Could Have Taken Out Entire Bronze Age Civilization, New Research Reveals
Meteor strikes on the Earth are incredibly rare. It seems this is just as well as their effects on a planet can be catastrophic. For example, the Chicxulub event, which may have effectively eliminated the dinosaurs and brought about the mammal-dominated age, is strongly linked to such an impact. However, it is apparent that large meteors can do damage, even if they do not hit the Earth. Even ones that remotely enter the atmosphere can wipe out a reasonably large area.
New “Candidate Super-Earth” Planet Found Near Barnard’s Star
A new possible planet around Barnard’s star has been discovered - a cold super-Earth with a minimum mass of 3.2 times that of Earth, orbiting near its snow line (the minimum distance from the star at which volatile compounds could condense). Apart from the Alpha Centauri system, which consists of three stars and is around 4.3 light years away from us, Barnard’s star is the next nearest star at 6 light years away.
A Dark Matter “Hurricane” Is Blowing Past The Earth Right Now
A team of researchers from the University of Zaragoza, King's College London and the Institute of Astronomy in the UK, led by Ciaran O'Hare, found a collection of stars that were all moving in the same direction. They called this the S1 stream, and these stars are believed to be the remnants of a dwarf galaxy that was swallowed by the Milky Way, billions of years ago.
How Did The Earth Get Its Water? Scientists Devise New Model of Planetary Oceanic Formation
Why is water so abundant on Earth, especially when it tends not to be so on other planets in our solar system?
There are a number of theories that may explain how the planet got its surface water. The scientists behind this particular hypothesis think of the total sum of this water as a singular planetary ocean. Besides this, there is at least one more global ocean on the planet, which is found in the Earth’s mantle (or inner layer) dissolved among its rocks.
Asteroids Fly Close To The Earth In November 2018 – Anything To Worry About?
You may or may not have read the news about the asteroids that flew extremely close to the Earth over the last few days (November 9-10, 2018). These bodies were believed to be as big as houses, and therefore, there was a compelling reason to worry that they may encroach on our atmosphere or something similar.
However, most of these scary super-close space missiles are not capable of harming us at all.
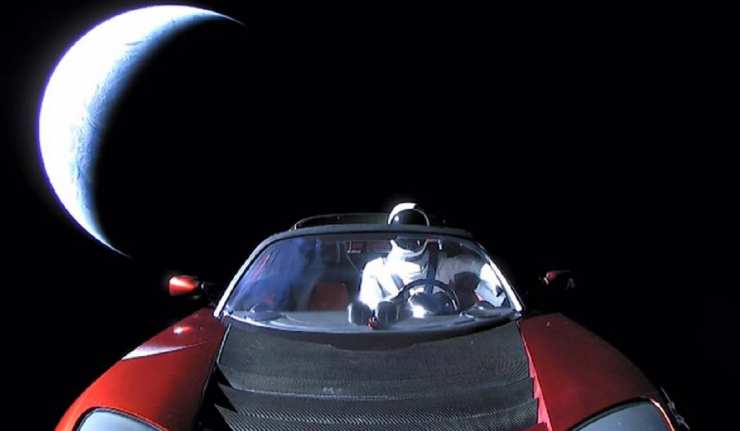
Drifting ‘Starman’: Tesla’s Space Roadster Reported To Have Passed Mars
Remember when Tesla blasted one of its cars into space? SpaceX, which, like Tesla, is owned by billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk, performed this stunt in February 2018. This was done to raise awareness of the company’s plans for crewed missions to destinations like Mars. Also, there was room in the payload of an unmanned launch that was scheduled for February 6, 2018.
World Biodiversity Loss By 60% As Per WWF: Our Planet At Critical Crossroads
The worldwide population of mammals, birds, fish and aquatic creatures, amphibians, and reptiles have plunged by almost 60 percent, since 1970, as human activities are continuing to overwhelm the environment, said the WWF conservation group, last week.
Stau Sleptons: The Bizarre Particles Blasting Out Of Antarctica And Changing The Face Of Modern Physics
Physicists have detected something mysterious coming from Antarctica’s frozen ground, a sort of cosmic ray - a light energy particle that has blasted its way through space, into the Earth.
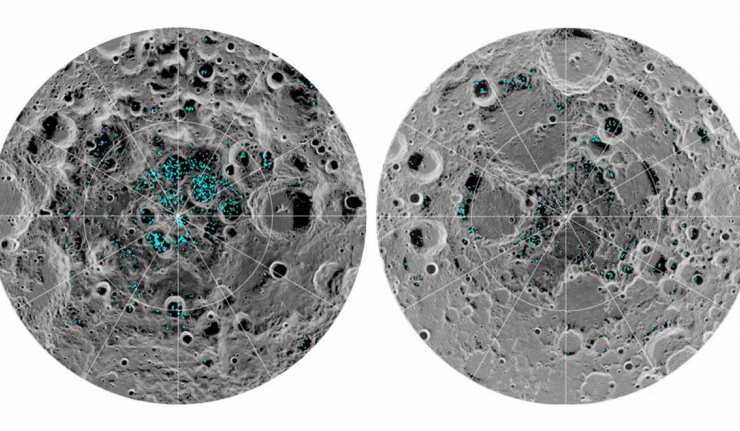
It Is Official: Water Ice Confirmed On The Earth’s Moon
It was Neil Armstrong who, after stepping on the moon, said, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” But it definitely seems as though modern-day science and the researchers of today have already achieved goals bigger than ever imagined!
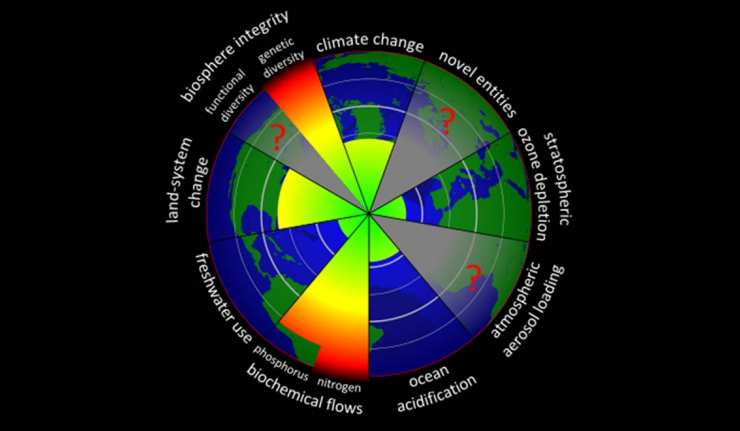
Sustainable Science: Exploring The Safe Operating Space For Humanity In The Anthropocene
The concept of carrying capacity is employed in a remarkably wide range of disciplines and debates, and it has been forcefully critiqued within numerous fields. Though, its historical origins still remain obscure.
The natural and engineering sciences offer tremendous prospect for contribution to a more sustainable future, and it becomes a responsibility because these areas produce, not only solutions but also, problems. It is much needed that science and technology are accompanied by societal priorities because this gives sustainability science its context and rationale.