health
ExPecto: New AI Predicts Biological Roles Of Genetic Variations
There are thousands of known genes in the human genome. This number refers to the DNA sequences that code for actual proteins, which carry out functions in the body once expressed. These genes can, in turn, experience millions of variations, which may cause the said proteins to turn out differently than their original DNA "blueprint." In some cases, these abnormal proteins may be the basis of a disease state.
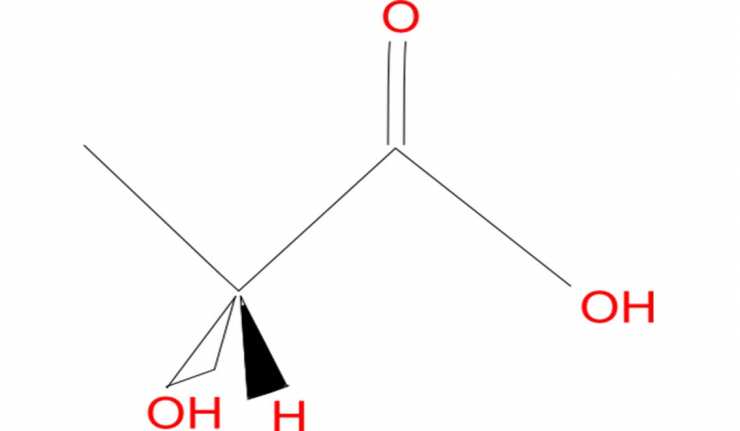
Reimagining Lactate: From Bio-Distress Signal To Potential Healer
If someone were to mention the word ‘lactate’ in conversation, you might be inclined to think about why people have stitches in their sides after running.
Classical secondary and tertiary education has taught us that lactate is a kind of muscle-cell waste product that may also be a marker of stress or illness. However, the study of this versatile biochemical product has experienced a considerable upheaval. This concern is due to the re-examining of some possibly faulty correlations made about the molecule and its roles in health and disease.
Research Finds That Sleeping Sickness Disrupts The Body’s Internal Clock
The condition associated with Trypanosoma brucei is known as sleeping sickness, where affected humans tend to want to sleep during the day rather than the night. Patients with this condition also exhibit altered patterns of body temperature and endocrine functions. Their activities gradually shift through the morning, which, in turn, increases the body's drive to go to sleep at the "end" of that day.
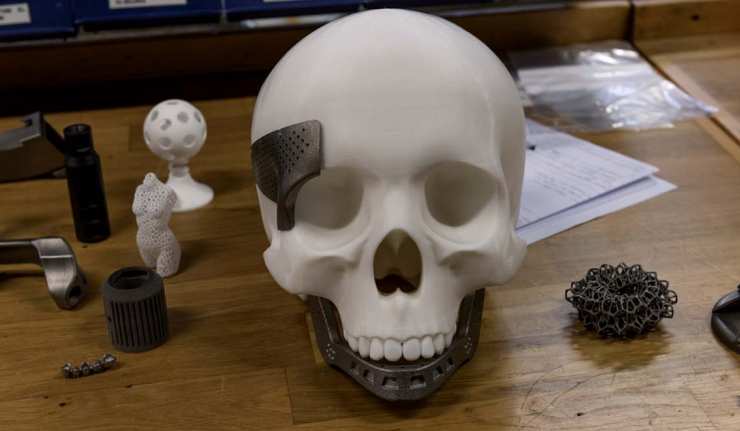
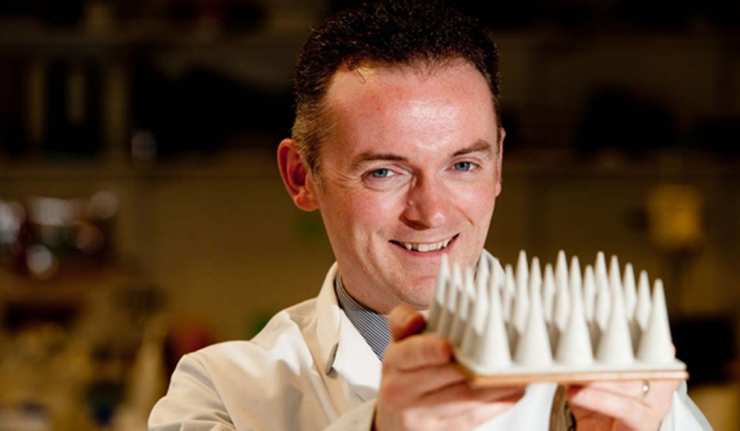
3D Printing to Heal Skull Fractures
The 47th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) is currently taking place in Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and has already turned out some interesting new findings.
For example, one presentation indicates that certain types of bone damage can be healed using a form of 3D printing. The project being showcased in this instance is intended to address skull bone defects, which are difficult to treat with conventional surgery.
True Biological Age Can Be Revealed By…Urine Test
Even though the process of ageing differs among individuals (based on their lifestyles and environment), it is inevitable and irreversible for all of them. Chronological age can be measured according to birth date, each year, but experts have adjudged this method to be inaccurate while determining true biological age.
Alcohol Makes Your Heart Go Faster: New Research May Link Binge Drinking to an Accelerated Heart Rate
The third week of March may be a time for celebration for many reasons. Those not enjoying a relatively extensive festival of national culture may instead feel the need to mark the results of certain marquee sporting events. If you chose to celebrate “St. Patrick’s” weekend with a few drinks, we here at ES hope you enjoyed the use of moderation as well. Recent research suggests that consuming alcohol in large amounts is not conducive to ideal health – even if it’s done in one-off bursts as rare events.
23andMe Cancer Risk Test Kit Gets A ‘Go’ Signal From FDA
One of the biggest challenges faced by cancer patients today is diagnosis of their condition early enough to get suitable treatment options.
Cancer results in more than 8 million deaths worldwide, each year, and the National Cancer Institute has predicted the numbers to rise to 22 million in the next few decades.
Among years of innovation and research, a new way to tackle the detection of this disease has been developed — an improved and faster screening test.
New Findings in Motor Neurone Disease Research Outlines Abnormalities in Important Nerve Cells
Motor neurone disease (MND), also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, is a condition in which patients lose motor independence. This is followed by systematic muscle wastage, which may leave affected people immobile for life. The mechanism and progression of MND has been studied in detail over the last few decades. This body of research has offered a great deal of insight into how cellular energetics, growth and activity contribute to the loss of motor function. In addition, certain specific genes (e.g. SOD1) may play a role in some cases of MND.
Seeing What Others See: Human Visual Information Converted into External Images
Using neuroscience to assess the perceptions of others in more and more direct ways may seem possible, but only in the realms of science fiction.
But now, a team of Canadian researchers have brought such technology closer to reality through the conversion of visual data from human participants into corresponding images on a screen.
Do Antidepressants Really Work? New Study Suggests They Do
According to the World Health Organization, depression is a common mental disorder that is the leading cause of disability, globally. This condition, often leading to suicide among ages between 15 and 29, is known to affect more than 350 million people worldwide.
New Technique Brings Adult Stem Cell Technology Closer to the Everyday Clinic
Stem cell technology has seen vast advancements as a result of the discovery of the Yamanaka factors. They are a group of four transcription factors that can be activated to convert an adult cell into a usable stem cell.
Gene Therapy for Inherited Retinal Dystrophies Licensed by Novartis
Contributing to less than 200,000 cases per year in the US, retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a type of retinal dystrophy that results in blindness from a loss of function in the retina.
There is no cure for this condition yet, just the treatment of its symptoms. Like RP, there are several other inherited retinal diseases like Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), which requires the attention of researchers and drug manufacturers.
Helping Veterans with PTSD: Support From Service Dogs
For war veterans suffering from posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), navigating through life after returning home from active combat can be a difficult and challenging process.
PTSD can manifest itself in any number of ways: disturbing flashbacks, feeling on edge and difficulty sleeping are all common symptoms of this invisible disorder.
Gold Dirt: New Class of Antibiotics Isolated From Soil-Based Sources
If someone were to ask you where the hope for the future of antibiotic drugs was going to come from, your answer probably would be anything besides ‘soil’.
On the other hand, you may also have known that some extremely dangerous bacteria (such as those associated with the disease tetanus) are also found in this substance; therefore, it may be reasonable to assume that some soil-living micro-organisms may have evolved chemical defences against others.
The Simple Blood Test for Alzheimer’s is Nearly Here: Researchers Prove Their Plasma Analysis is Comparable to Diagnostic Standard
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most prominent and well-known progressive neurodegenerative conditions that affect humanity.
It is a form of dementia related to excessive levels of proteins such as tau and amyloid-beta in certain brain regions. Treatment for AD is gradually becoming more and more effective; with many more patients capable of living more or less normal lives while managing their conditions over time.
New Study Challenges Role of Mutation Rates in Age-Related Cancers
The risk of developing many different forms of cancer may be strongly associated with age. Some scientists even agree that there may be a “power law” that connects increasing age to increasing susceptibilities to cancer. However, a new study, conducted at Dundee University, disrupts this theory with evidence of a new statistical link between thymic functions and the age-related risk of cancer. This new data may be the basis of a new, immune system-based hypothesis to be used in the study and treatment of relevant diseases.
Investigating Drug-Resistant Strains of Leprosy Bacteria
Leprosy, caused by Mycobacterium leprae has been around since time immemorial, or in fact the Iron Age, to be exact.
Although curable with MDT (multidrug therapy) in the early stages, the disease severely affects the lungs, skin and eyes, and in extreme cases, results in disability. There are more than 200,000 cases of leprosy reported, every year, in countries of South America and Asia.
Experts are trying to gain insights into the bacteria’s drug-resistant strains, its origin and evolution, which could lead to the elimination of the disease in the long-run.
Novel Skin Patch: The Future of Antibiotic Treatment?
The resistance to antibiotic medications is an ever-more prominent public health issue. This phenomenon is related to the acquisition of novel properties or adaptations that allow bacteria to avoid death caused by these drugs.
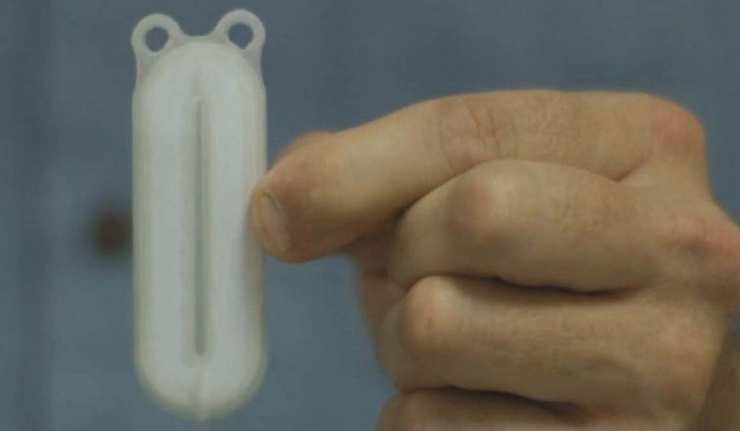
New Removable Implants for Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the patient’s ability to produce insulin is negated by their body’s own protective processes, often from an early age. As with type 2 diabetes, it can require chronic medical treatment from the point of diagnosis in order to avoid severe, even life-threatening, disease events.
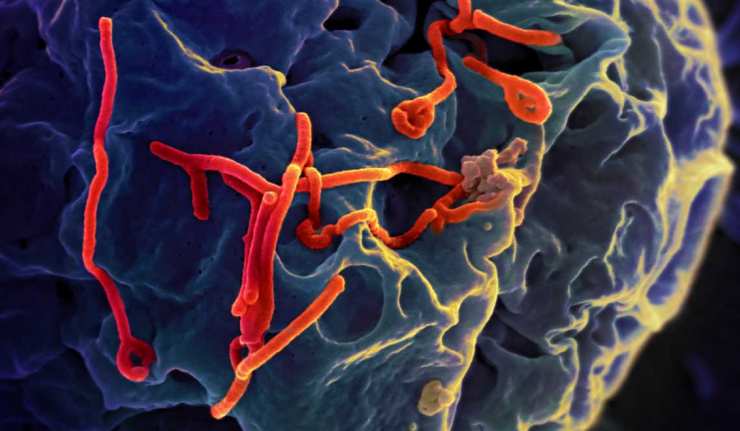
Research Shows That The Ebola Virus Can Be Inhibited
The first cases of Ebola virus disease (EVD) were registered in Africa’s Sudan and Congo, and since then it has spread by contamination and human-to-human transmission to several parts of West Africa and surrounding regions.
Hailing from the Filoviridae family, the disease is incurable and, most often, fatal.