Science
Manganese Orbs For Tumor Imaging and Treatment
Today, there are many projects that investigate new and emerging treatments that address a critical factor in cancer progression: the tumor microenvironment. This is a complex process, in which cancer cells adjust the conditions within, and also possibly in the immediate vicinity of, the tumor they have formed to their own ‘liking’. Tumors develop their own internal environments for a number of reasons, which include resistance to aspects of the patient’s immune system which could be capable of destroying or damaging them otherwise.
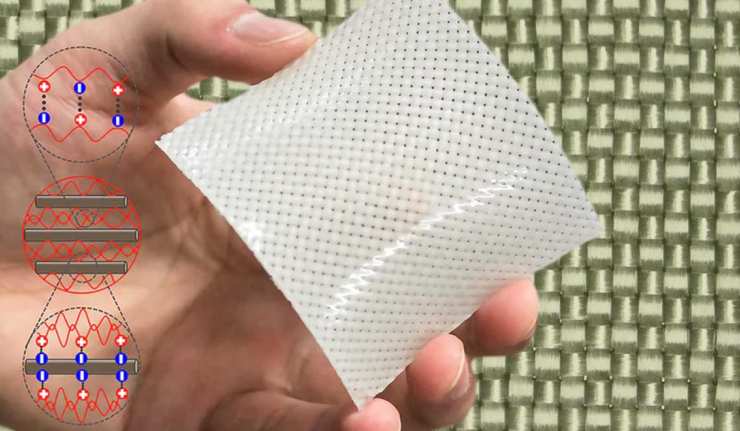
Synthetic Polymers Revolution: The Strength Of The Hydrogel Fibers
Many material scientists and engineers work with the goal of making synthetic polymers with the strength and conformation to rival or exceed natural products such as silk. This is done to create textiles, sheets or other implements to be used in construction or outerwear for their durability, strength and longevity. Unfortunately, though, there are often drawbacks linked to the compounds these researchers develop. They may be made from toxic substances, be expensive to manufacture, or require a large amount of energy in their formation.
The Breakthrough Prize: The Oscars of Science Celebrates The Scientists Who Shape Our Future
Last night, the Breakthrough Foundation hosted an awards ceremony in Silicon Valley, where $22 million in prize money was awarded to a huge variety of scientists for their ground breaking research efforts.
‘I, Cyborg’ To Be Controlled By Living Brain Cells
In 1960, scientists Manfred Clynes and Nathan Kline described the idea of an enhanced human being that can survive in alternate or extraterrestrial environments as: “For the exogenously extended organizational complex functioning as an integrated homeostatic system unconsciously, we propose the term ‘Cyborg’”. In layman terms, also called android, a cyborg or a cybernetic organism, would be referred to as, any entity with both artificial and biological parts and as defined by the Oxford Dictionary, a “man-machine”.
New Sequencing Technique Improves Accuracy in Human DNA Analysis
Conventional DNA sequencing is getting more powerful and time-effective. However, it is still based on amplification, which involves using a DNA polymerase such as Taq to produce numerous copies of the sequence to be analysed. The problem with amplification is that it can increase the risk of false-positive results in terms of pertinent mutations.
Writing Music with the Mind: New BCI Modality Offers the Power to Make Music as well as Play It
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) that allow people with severe neuromotor or motor disorders to communicate are becoming more and more common. This is realised by scanning brainwaves using electroencephalography (EEG) and converting them accurately into words, letters or other objects that the user intends to replicate in their minds. BCIs are beneficial for those with extensive paralysis, ‘locked-in’ syndrome and other similar conditions.
IBM’s Watson Helps Rapidly Identify Treatments for Cancer Patients
A new study suggests that IBM’s Artificial Intelligence (AI) Watson may well be a very useful tool for identifying possible therapeutic options for cancer patients.
The study was led by the University of North Carolina Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center and focused on the identification of possible treatment options based on the genetics of the patient’s tumor.
Secrets of Space Weather Revealed: Solar Storms
Whilst the sun might look relatively benign from here on Earth, in reality it’s a hugely powerful star which undergoes many storms, some of which scientists are only just beginning to understand.
Scientists can now predict the likelihood of coronal mass ejections, or CMEs with relative ease because these events are usually preceded by some kind of warning sign. This can include the presence of more energetic particles, bright flashes or bursts of heat.
Wheat Sensitivity = Gluten Intolerance? Maybe Not, According to New Study
Many people find that they have an adverse reaction to eating wheat, and may be advised to avoid high-gluten foods in the future. That is the conventional wisdom, developed as a result of a connection that has been forged between gluten and the impaired ability to process it as normal in some individuals.
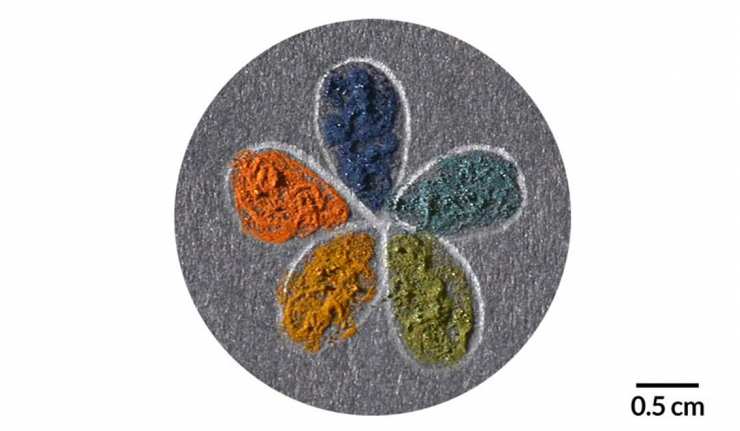
Synthetic Colors Based on Nature
Why would anyone apply advanced nano-science to the color of your car? There are a number of good reasons to do so, when you think about it. High-tech dyes could offer improved protection against fading, and preserve colors for longer. In addition, some colorants are metal oxides, which can be toxic to those who produce and work with these materials. Nanotechnology-generated dyes, on the other hand, do not necessarily require these ingredients. In fact, they can be designed so as to mimic natural pigments as much as possible.
XFEL is Online: Free Electron Laser in the World is Open for Business!
For twenty years, DESY (the German synchrotron administration) has been working on a bigger and better X-ray laser. Such an implementation would enhance the imaging and analysis of subjects from a wide range of scientific research topics, from viruses to exo-planets. The new laser, known as European XFEL, is based at the DESY research center in Hamburg, but extends nearly four kilometers along the ground until it reaches a campus in the Schleswig-Holstein town of Schenefeld.
New Research Indicates Yet More Negative Effects of Sleep Deprivation for the Brain
Sleep deprivation is regarded as a major public health issue, by those who study it and its effects at least. Research has shown that life-threatening mistakes for patients made by resident physicians can increase as much as seven times over in response to sleep-robbing schedules for these doctors. Sleep deprivation is linked to deficits in cognition, memory and vigilance, and is as a result discouraged in people who work in areas such as heavy industry and nuclear power.
Electronic Anticipation: How Computers Will Learn to Imitate Human Behaviour
You may have heard of advanced Bayesian calculations (ABCs), perhaps in the context of how computers are used to study climate patterns and how these will change in the near future. ABC is the basis for how computers can achieve inference as a result of the data it is fed. Inference is an important part of the process by which predictions that our brains make on an everyday basis match up with the available objective evidence.
Musk on Mars: Closer than Ever?
Are you ready to pack up and go to live on a Martian colony? Elon Musk thinks you should be.
Unlocking The Fountain Of Youth: Stem Cells May Hold The Key
Many of us might wish that we had the same energy levels and good health that we enjoyed when we were younger, but we know that the passage of time affects us all eventually. Now though, new research has uncovered a potential therapy to reverse at least some of the effects associated with growing older.
A New Field of Science Opened Up Thanks To LIGO and VIRGO
In a press conference today, scientists from over 70 different observatories came together to reveal new information about the nature of our universe.
The Flight of the Albatross: Secrets of Wind-powered Flight Revealed
It might seem that the kinematics of exactly how albatross maintain their flight over hundreds of miles per day would only be of interest to biologists however, a team of engineers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have found that the flight patterns of these gigantic birds could well be used for a number of applications in other areas of scientific research.
Close Encounters With An Asteroid Allow For International Collaboration
On Thursday October 12, a small asteroid estimated to be between 10 and 30 meters in size is going to be the subject of international attention as a global team of scientists observe its orbit past the Earth.
The asteroid, known as 2012 TC4, is due to pass us by at an altitude of around 44,000km (27,300 miles). This is lower than the altitude that the majority of geosynchronous satellites orbit the Earth. Its predicted that TC4 will be closest to the Earth as it passes just south of Australia, at around 05.41 GMT.
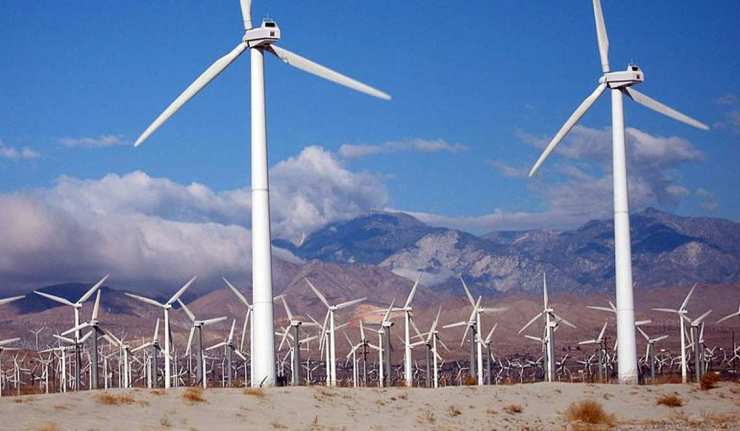
Powering The World With Wind Turbines
What if we could generate all the energy required to power the whole of civilization, just using wind turbines? It might sound far-fetched but new research published this week has suggested that this scenario is not entirely unrealistic.
A new location for wind farms
It would however, require some significant changes to the location of wind farms – placing these far out in deep water areas of our oceans, as opposed to on land or relatively near to the shore.
Graphene is the New Silicon? – A Closer Look at the Most Likely Next-Generation Superconductor
Graphene is a fascinating and relatively novel material that may have a whole range of applications in the areas of electronics and engineering in the near future. It is a superconductor that has recently demonstrated the ability to co-exist with silicon to enhance the capabilities of this complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS). These capabilities include photonics: for example, silicon/graphene transistors have recently formed the basis of a sensor that can ‘see’ visible, IR and UV light simultaneously.